The global economic order has witnessed significant transformations over the years, with the United States emerging as the dominant player in the 19th century. This was primarily led by factors such as USD becoming the world reserve currency and US having the world’s strongest military. However, recent developments have sparked anticipation of a power shift, as countries like China and India catch up. This article delves into the evolving dynamics, analyzing the factors contributing to China’s rise, India’s potential, and the challenges faced.
China’s Economic Ascent: A Manufacturing Powerhouse
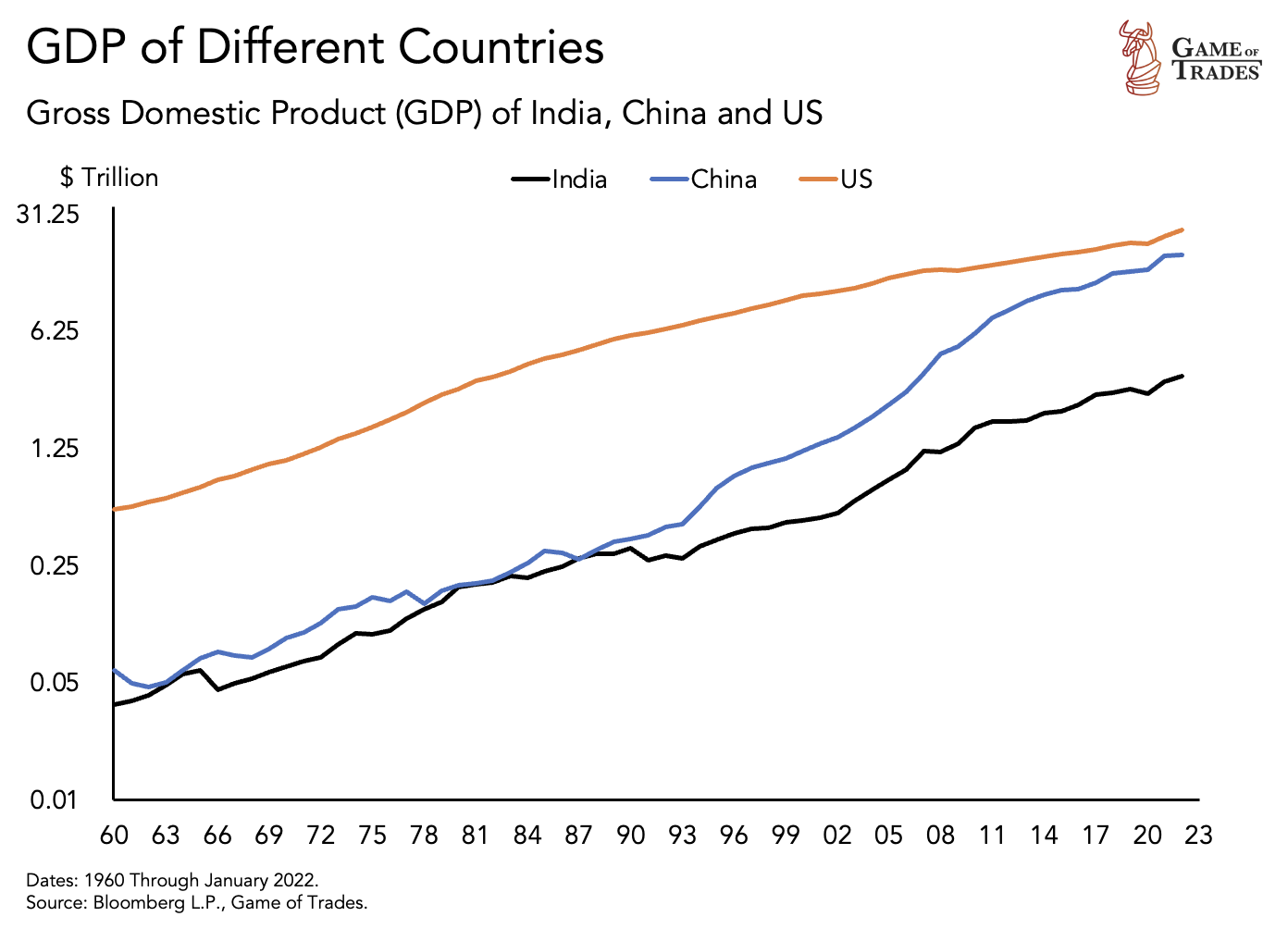
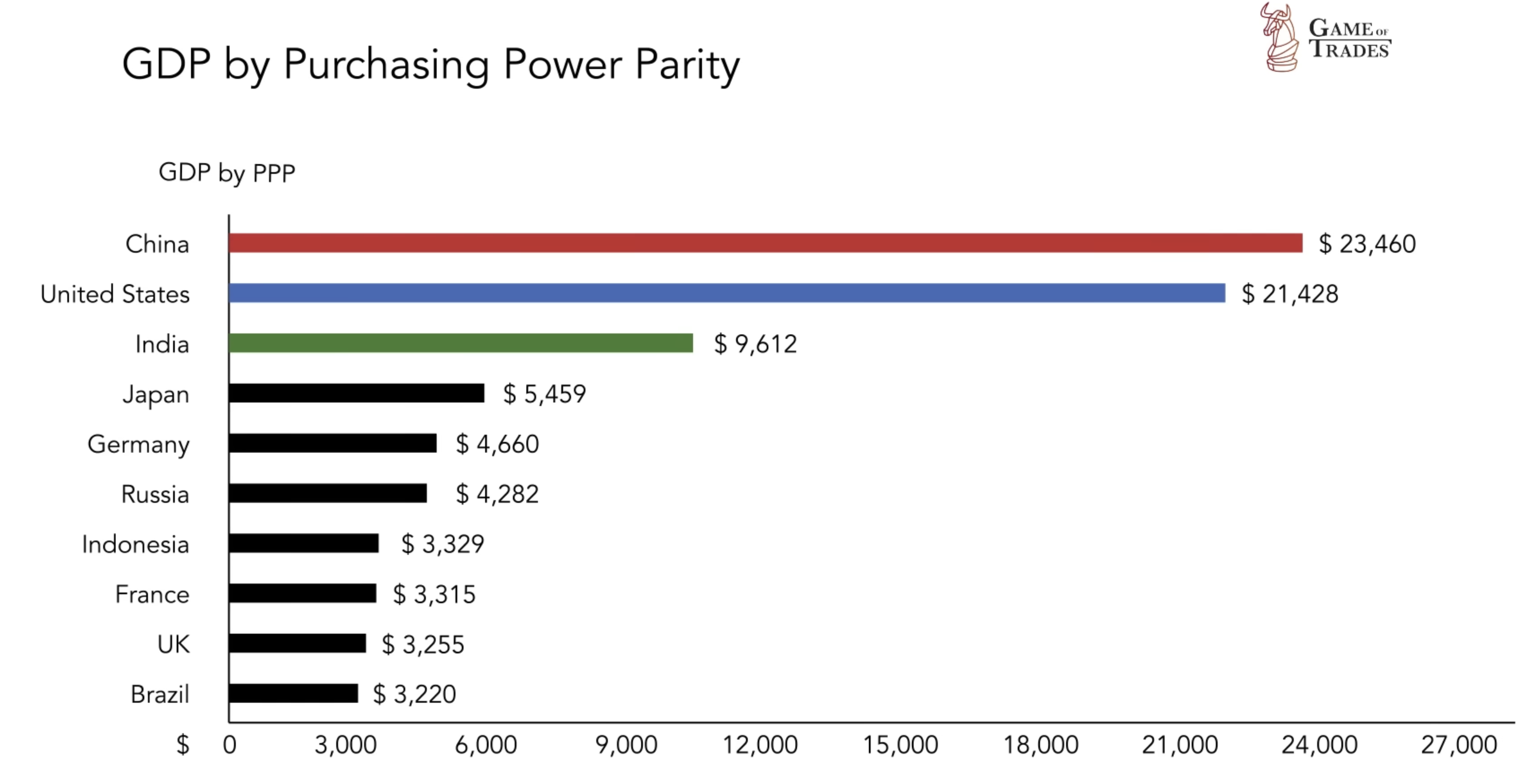
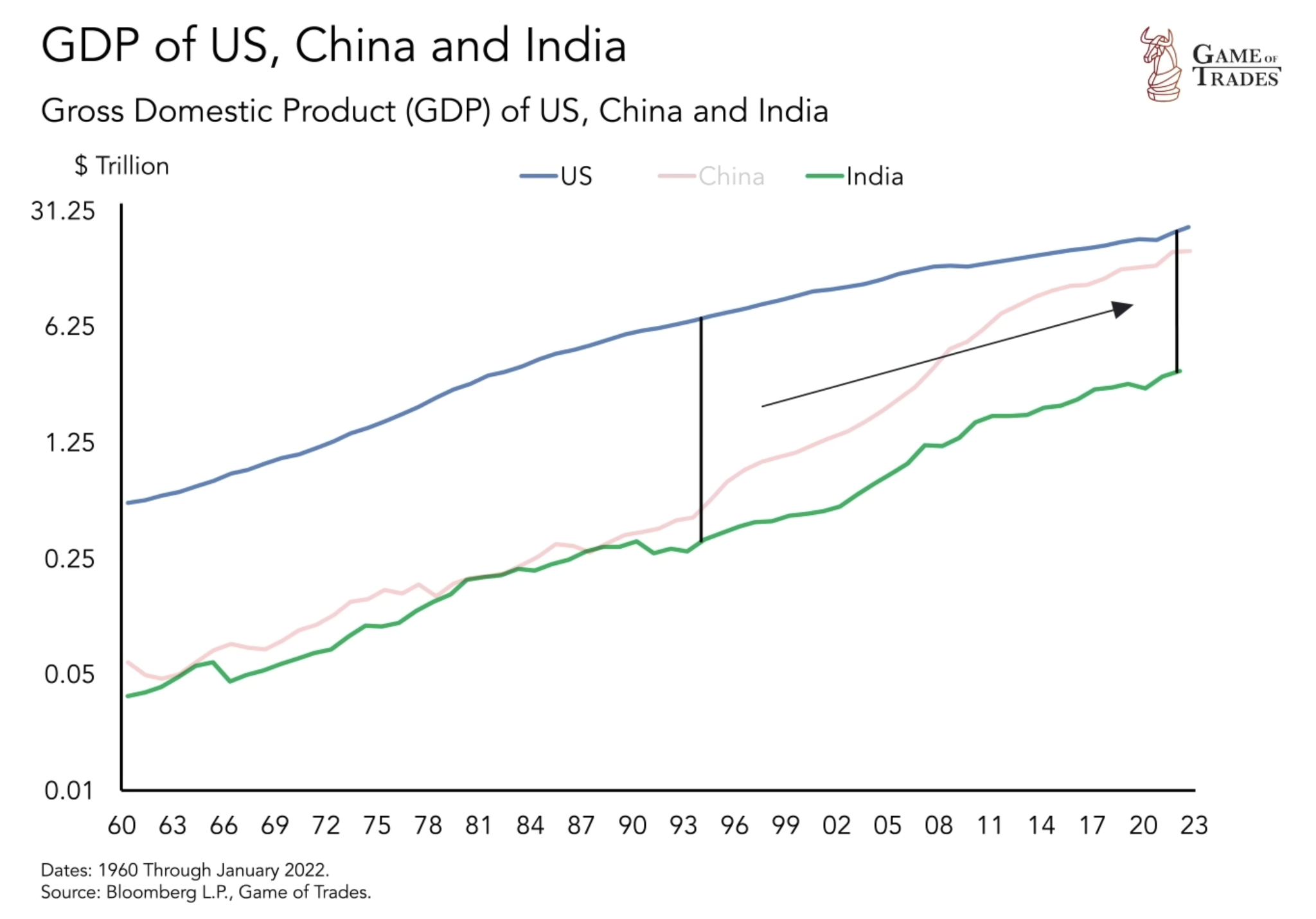
The US Stock Market, with 50% of the global market cap, holds immense influence. As other economies rise, speculation arises about the US transitioning from a giant to a less relevant player, similar to the UK’s trajectory in the 1900s. Signs of a shift are evident as China surpasses the US as the largest economy by GDP adjusted for purchasing power parity (cost of living), reaching $23.4 trillion.
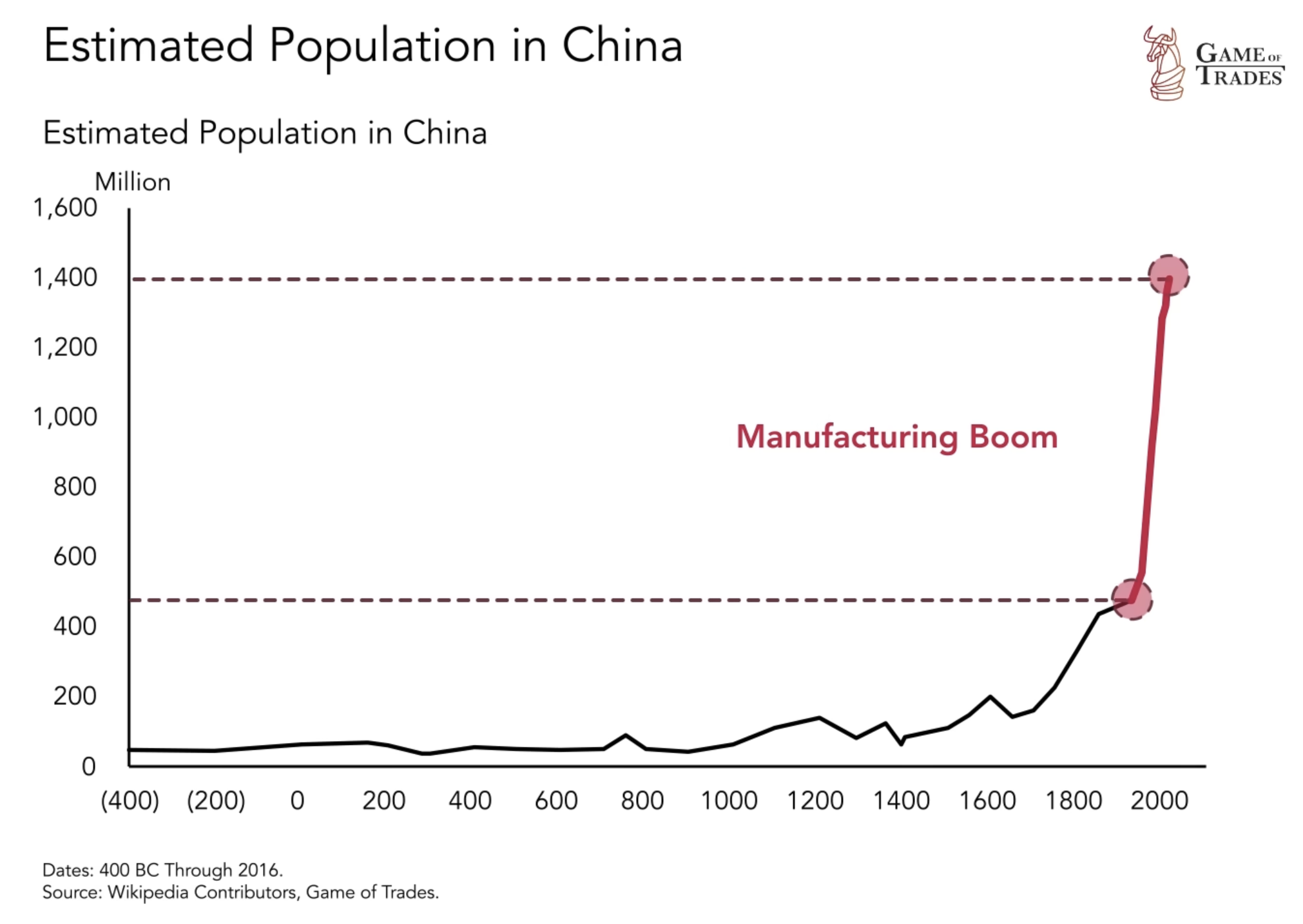
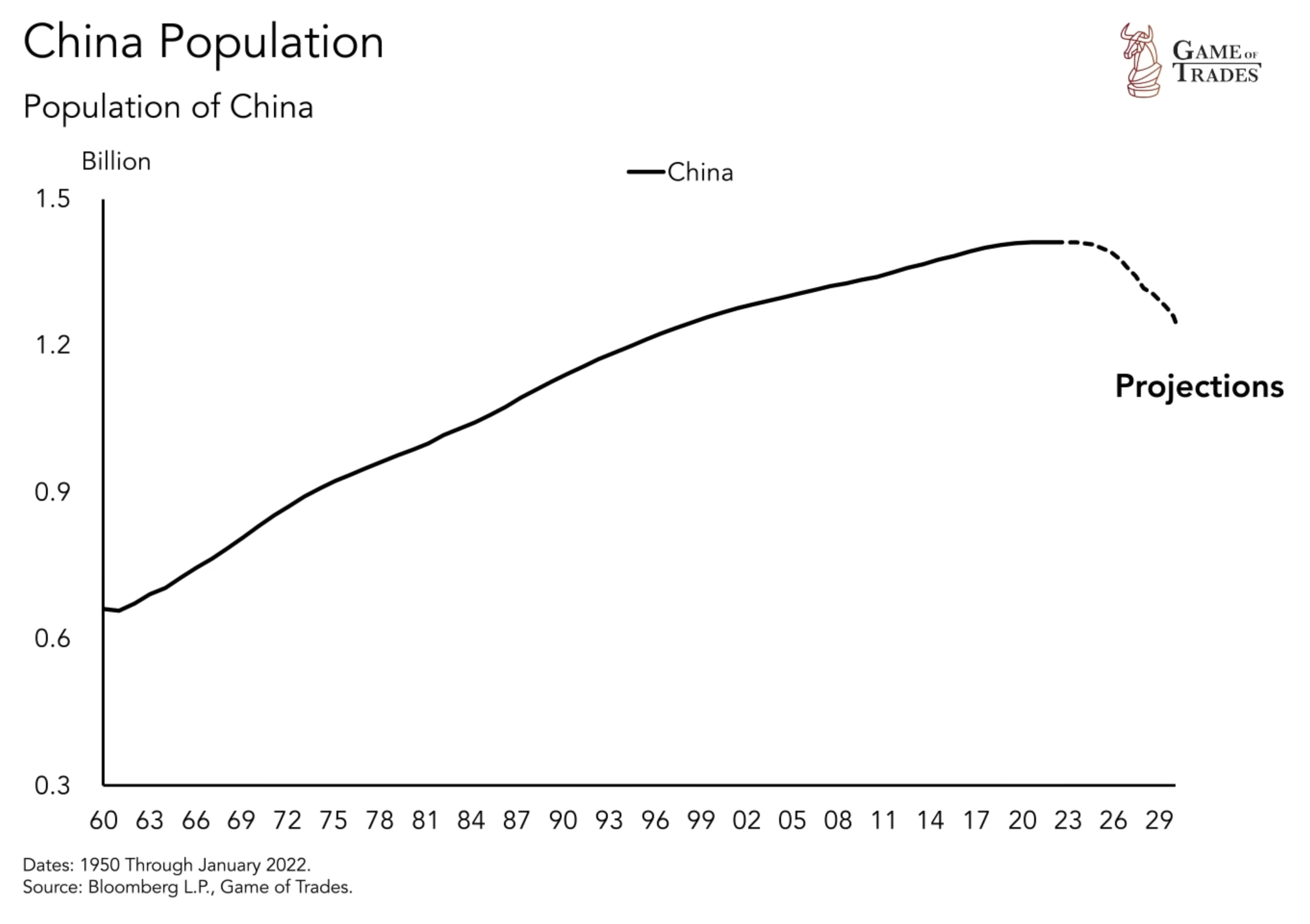
China’s remarkable journey to become a manufacturing powerhouse has been fueled by its exponential population growth. This population growth has not only contributed to the surge in China’s workforce, but it has also provided a vast consumer market for its products. With a population that has grown from 500 million people in 1950 to a staggering 1.4 billion, China has been able to leverage its vast labor force to flood global markets with cheap labor and goods. This flood of cheap labor and goods has had a profound impact on the United States’ manufacturing sector, which has experienced a significant decline as a result. The competition from China’s manufacturing industry has forced many American companies to outsource their production to China in order to remain competitive.
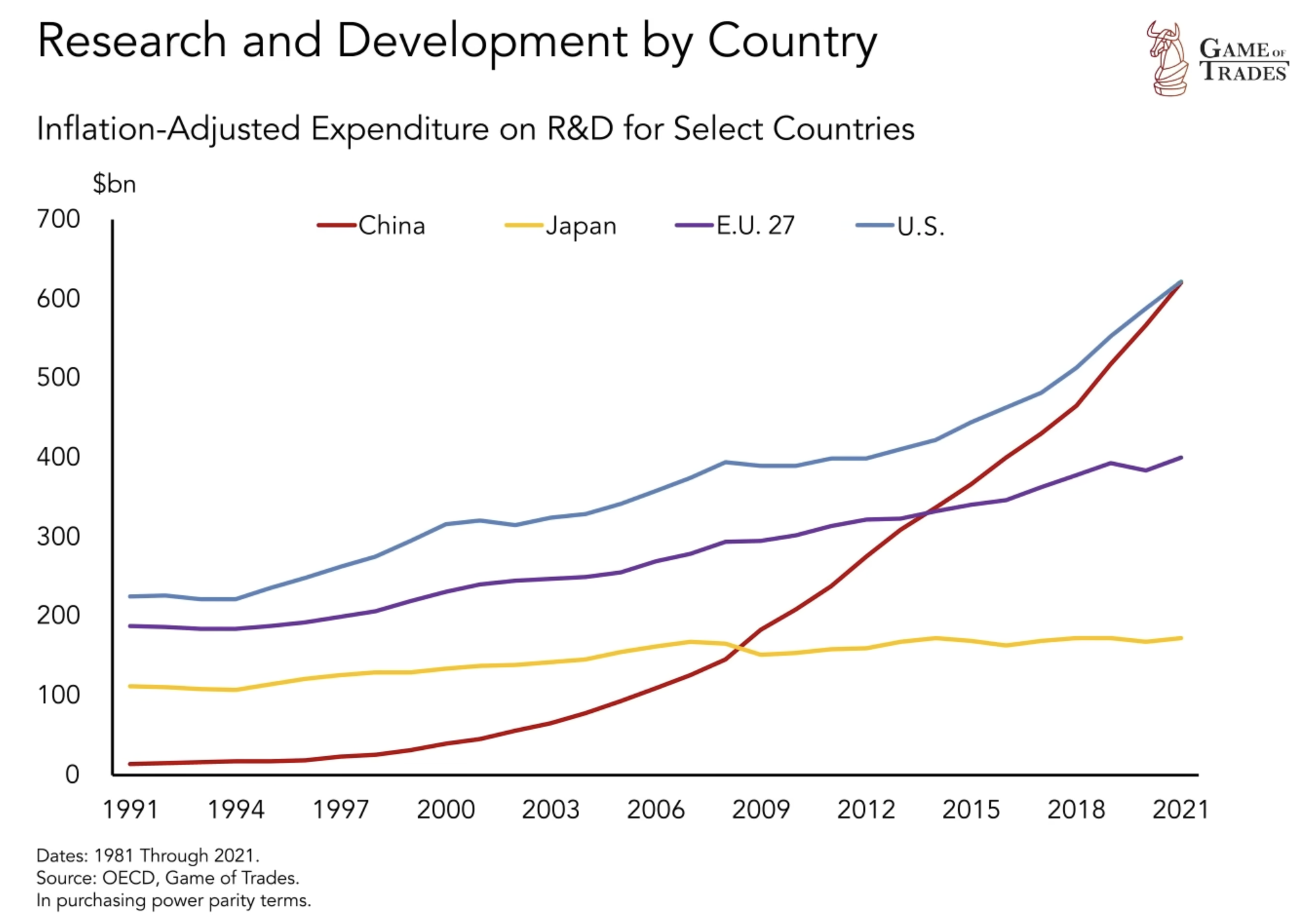
China’s economic surge has propelled remarkable growth over the past few decades. Since 1999, China’s GDP per capita has experienced a tremendous increase, soaring from $2,000 to an impressive $12,000 today. This significant rise in GDP per capita reflects the country’s commitment to economic development and progress. Additionally, China has made substantial investments in research and development (R&D) in recent years. Their annual investment in R&D has reached nearly $1 trillion, surpassing both Europe and Japan and closing in on the United States. This signifies China’s growing influence and competitiveness on the global stage.
Challenges Faced by China: Declining Population
As signs of a shift emerge, China has already surpassed the United States as the largest economy by GDP adjusted for purchasing power parity, but challenges lie ahead. Manufacturing makes up over 40% of China’s economy. As Chinese population’s wealth increases, production costs are likely to rise well potentially resulting in more expensive labor costs. Moreover, a declining population also poses demographic risks, similar to that experienced by Japan in the 1990s.
India’s Rising Potential: A Sustainable Trajectory
India’s unique economic trajectory differentiates it from China. With a diversified economy, India relies on services for 60% of its GDP, reducing its dependence on manufacturing. The GDP per capita, at $2200, also suggests significant room for growth. This sustainable approach, coupled with ample room for growth, positions India as a contender to catch up to both China and the United States.
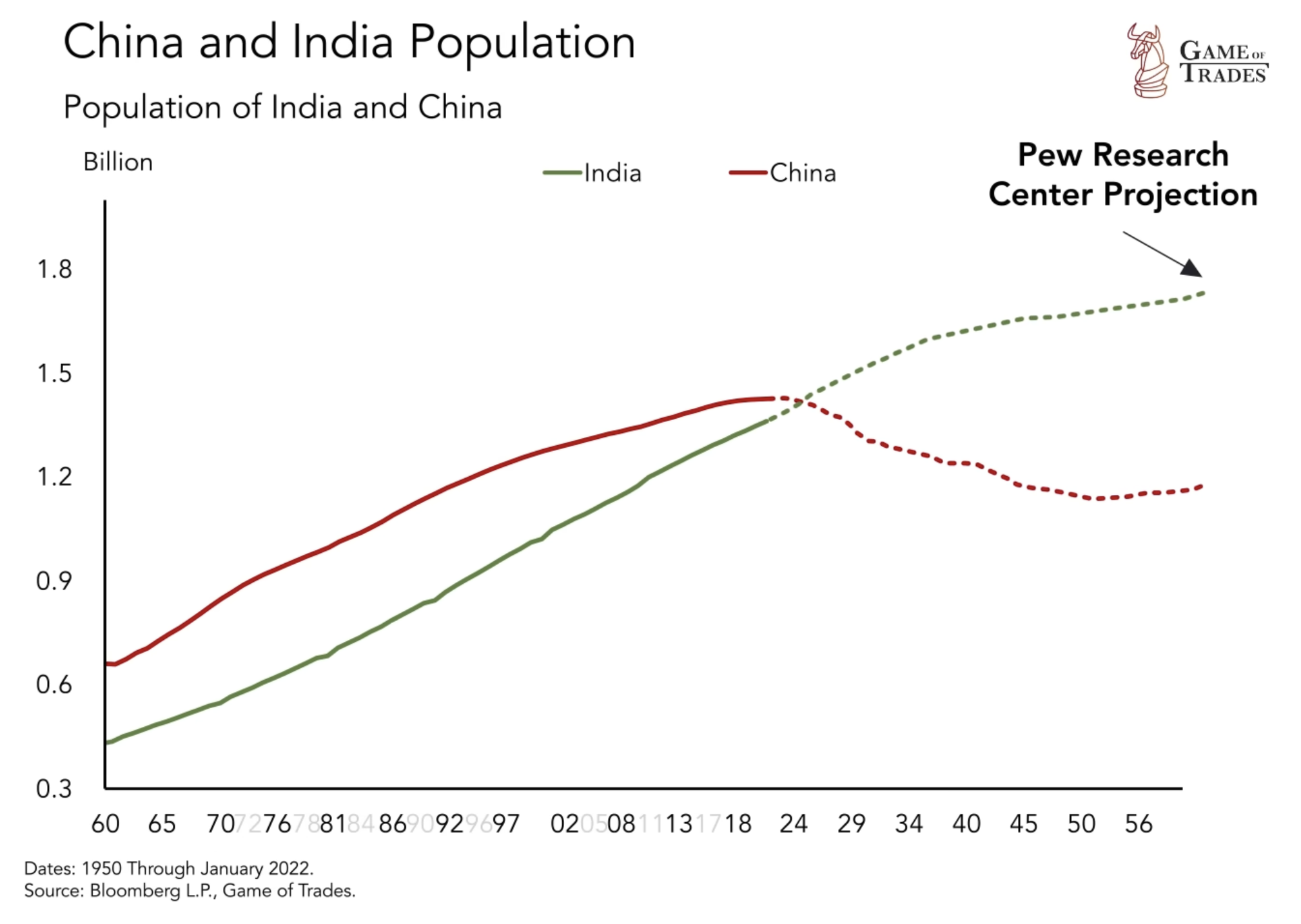
Moreover, it is worth noting that India’s population is projected to surpass that of China in the coming years, as reported by the Pew Research Center. This significant demographic shift is expected to continue until 2060, with India’s population continuing to rise steadily. This trend has far-reaching implications for various aspects of society, including the economy, healthcare, and social infrastructure.
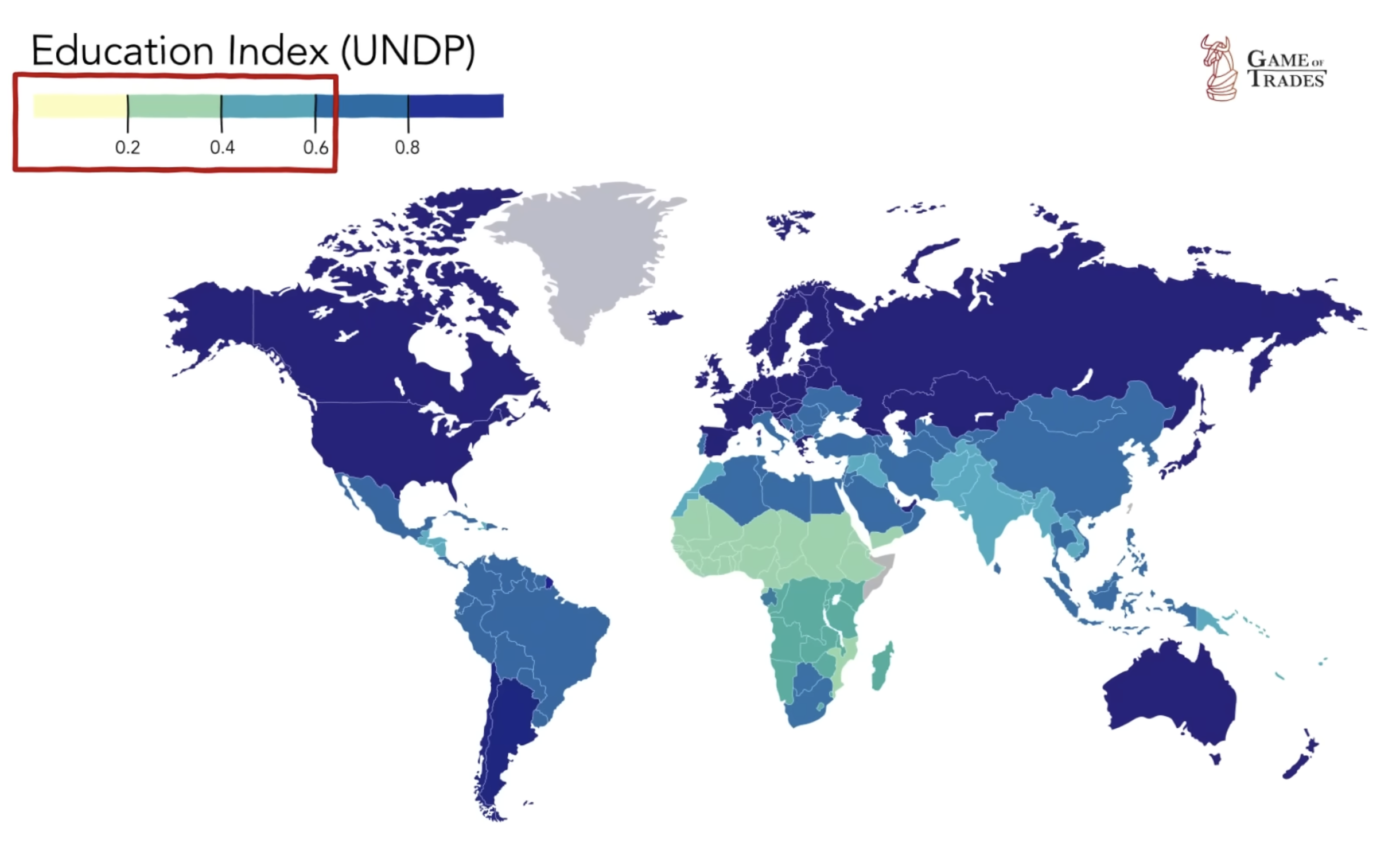
Challenges Faced by India: Education and Research
Despite its potential, India faces substantial challenges. The country’s education index calls for significant improvements. With an education index below 0.6, trailing even nations like Iraq and Ghana, India must ramp up investments in education and research to become a dominant economy.
The United States: Challenges Amidst Soaring Public Debt
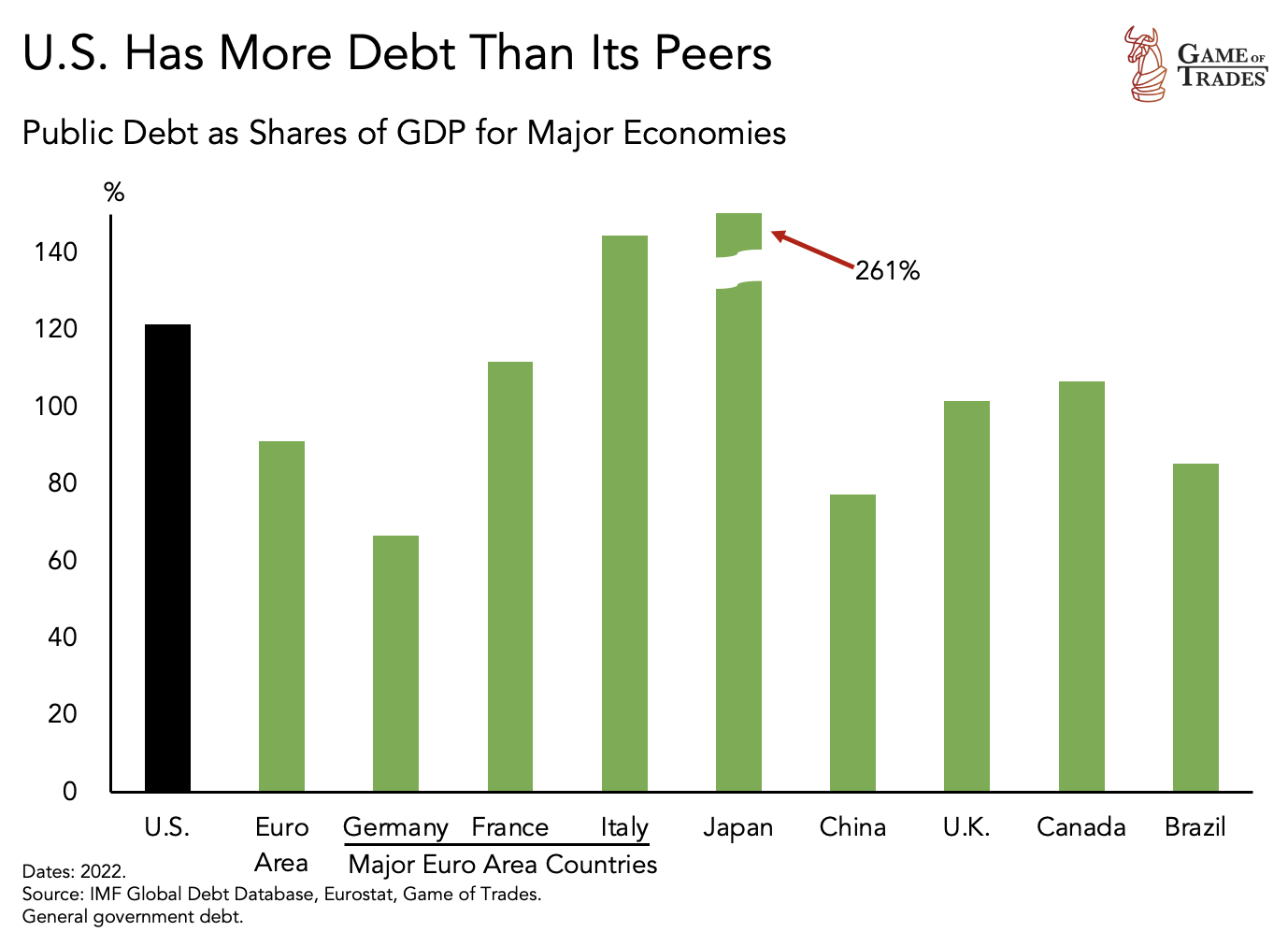
While China and India make progress, the United States grapples with its own challenges. One pressing concern is the soaring public debt, currently standing at 120% of GDP. Although countries like Italy and Japan exceed this figure, their economies are struggling. In contrast, China, with an 80% debt-to-GDP ratio, appears relatively more robust. Increasing debt often hampers growth as politicians raise taxes and cut spending to avoid a debt crisis. This causes a slowdown in long-term economic growth.
Conclusion
The global economic landscape is undergoing a transformative period, with China and India rising as potential economic powerhouses. While China’s manufacturing dominance and research investments position it as a formidable force, India’s sustainable trajectory and room for growth present a compelling narrative. However, both countries face significant challenges that require attention. As the United States confronts its own obstacles, such as mounting public debt, the future of its global dominance remains uncertain. Click here to get free trial for 7 days! Subscribe to our YouTube channel and Follow us on Twitter for more updates!



