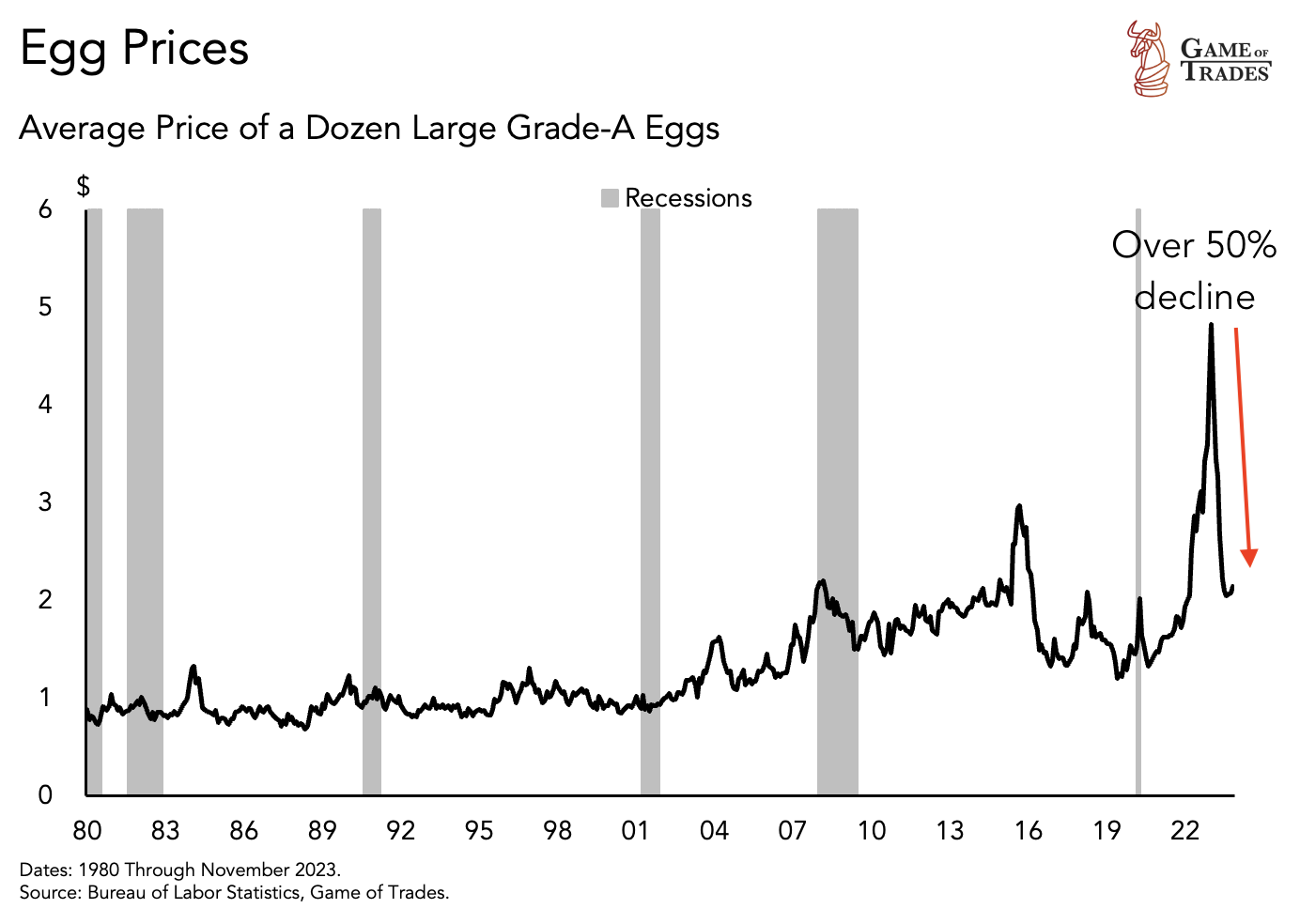
In the ever-evolving landscape of financial markets, recent years have witnessed notable declines in specific asset prices. Used car prices, for instance, have experienced a 25% drop since 2021, paralleled by a 50% decrease in egg prices in 2023. This has put the worries of deflation in the minds of investors.
Inflation and Its Reversal
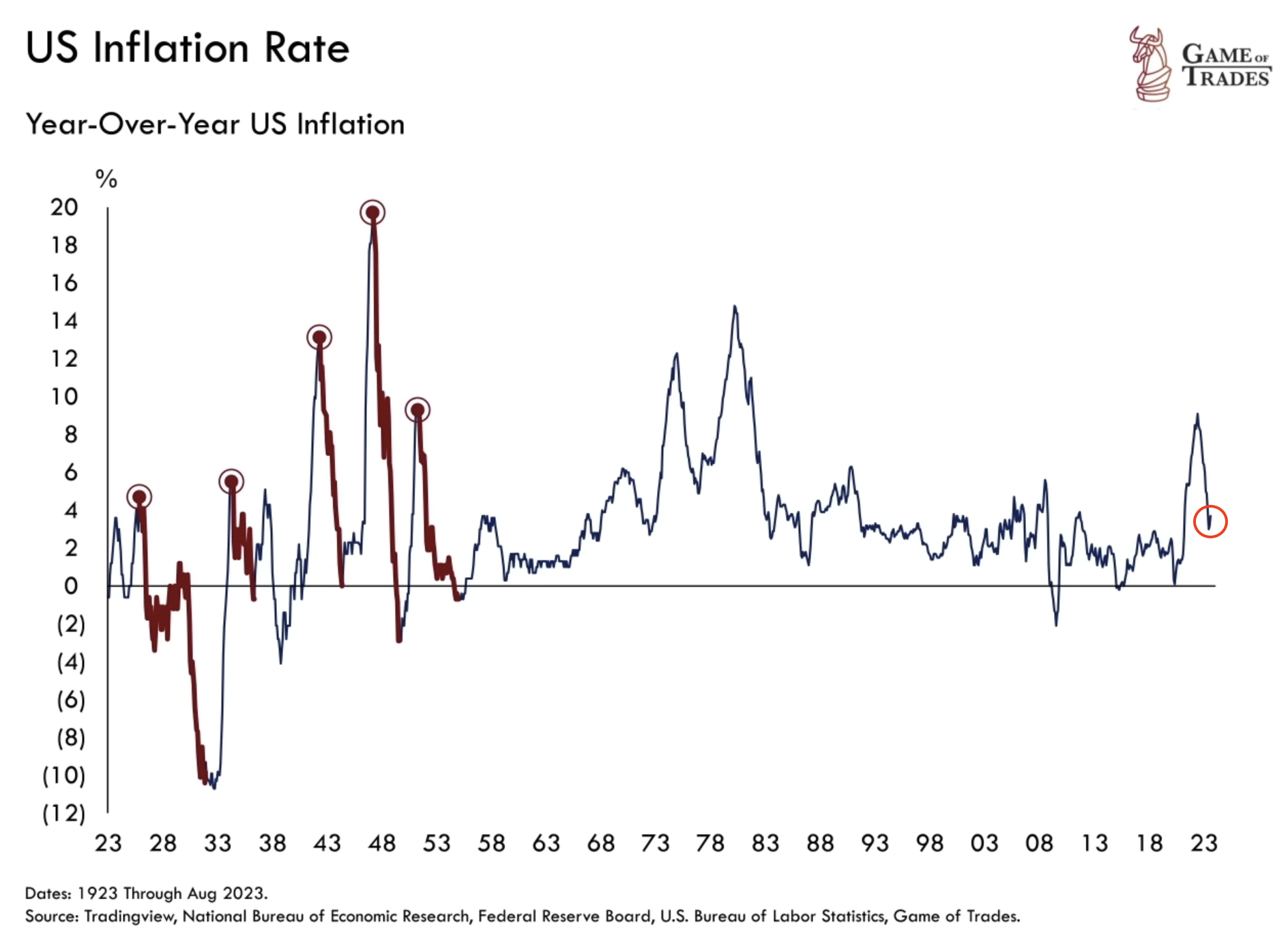
While inflation has been the recent norm, it’s essential to recognize that the reverse can occur when prices start contracting. The Great Depression serves as a historical example, where a 30% price drop unfolded in just three years. Brief instances of deflation also marked the financial landscapes of 2008 and 2015.
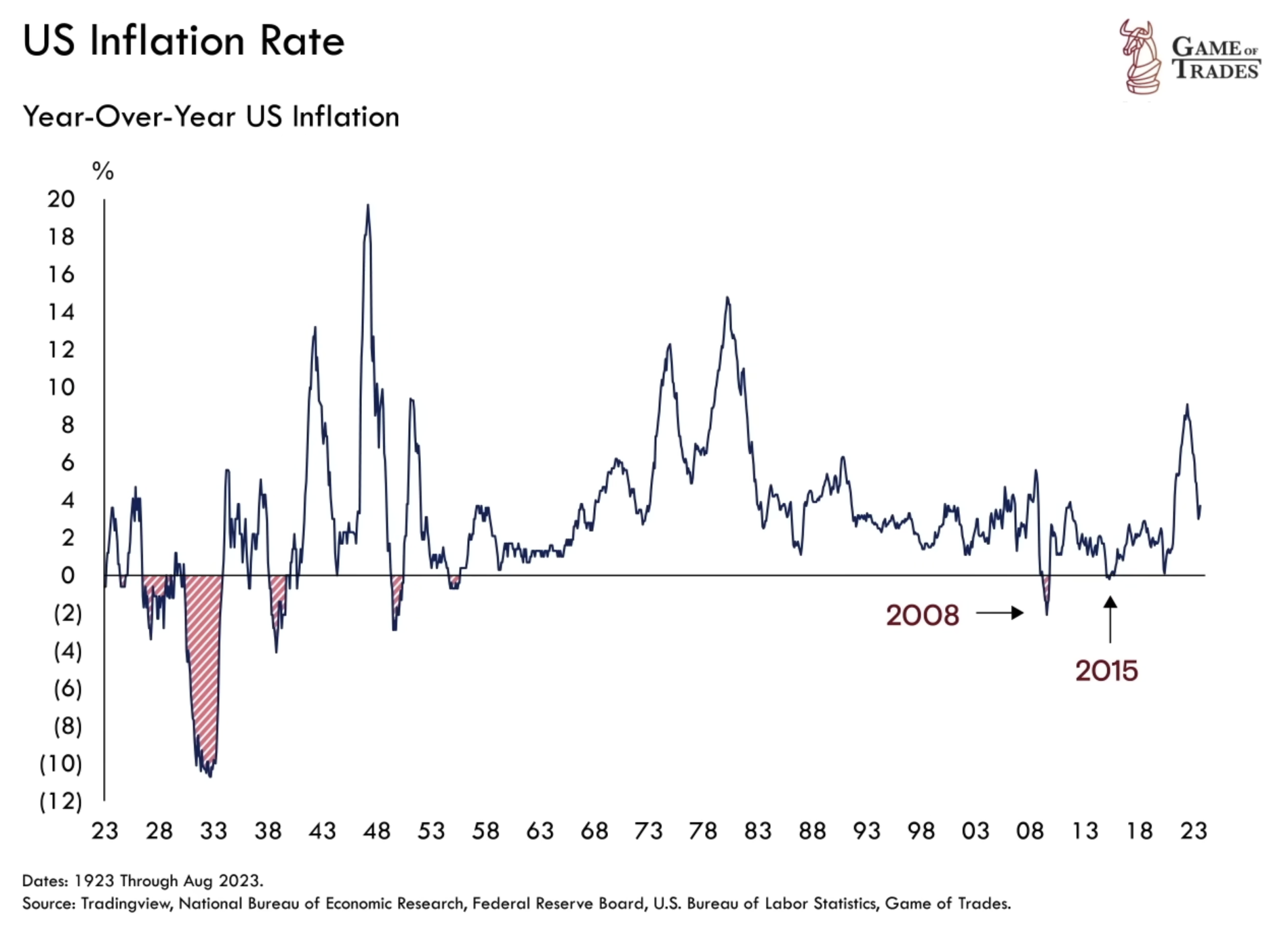
As of now, the inflation rate remains around 3%, a relatively high figure based on historical standards. However, some market experts argue that deflation may follow, a trend often observed after significant inflation spikes.
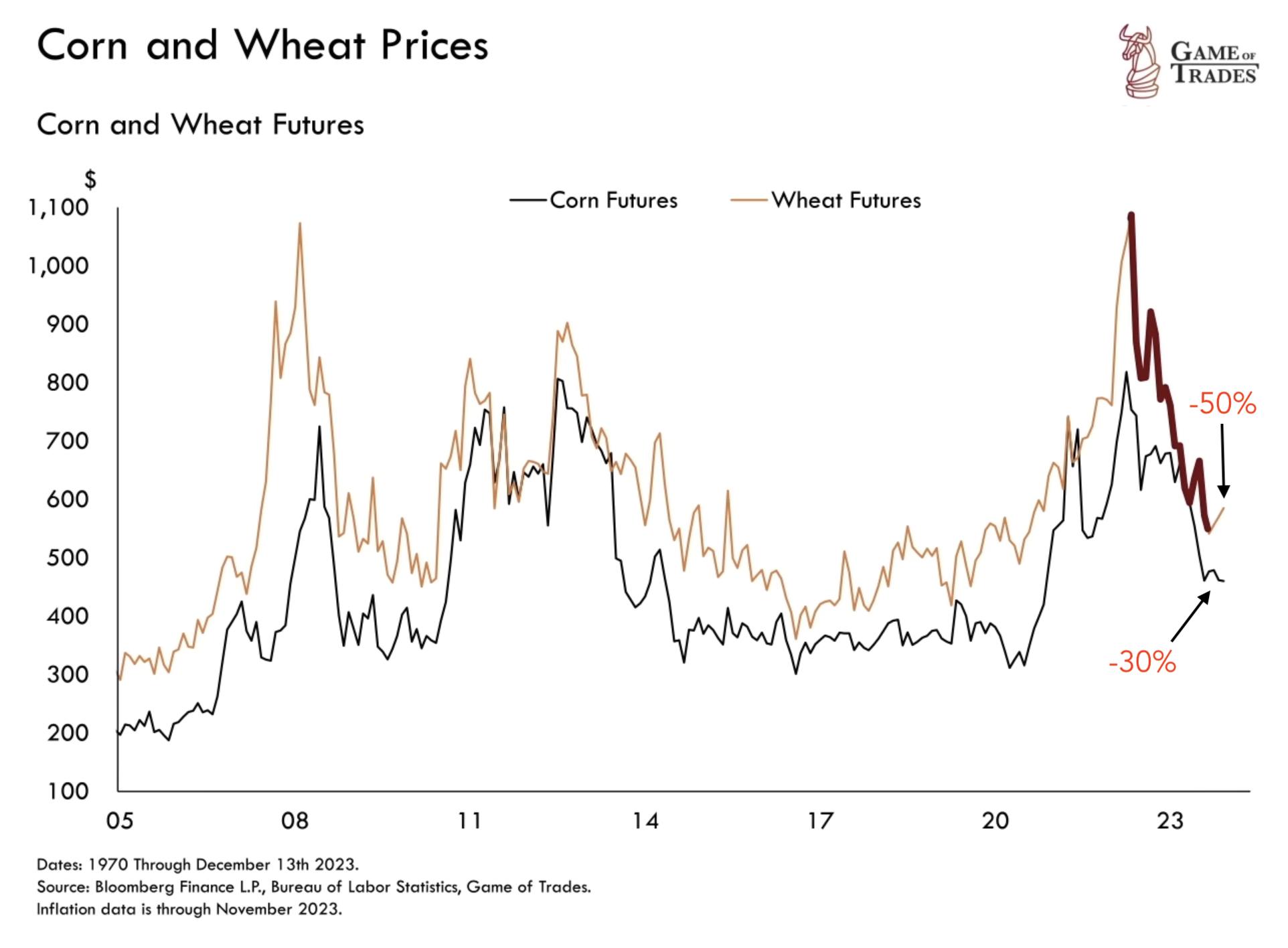
Corn prices have witnessed a 30% drop, and wheat prices are down 50% since May 2022. These staple crops, constituting a substantial portion of global calorie intake, played a role in driving inflation in 2022 but are now contributing to its decline.
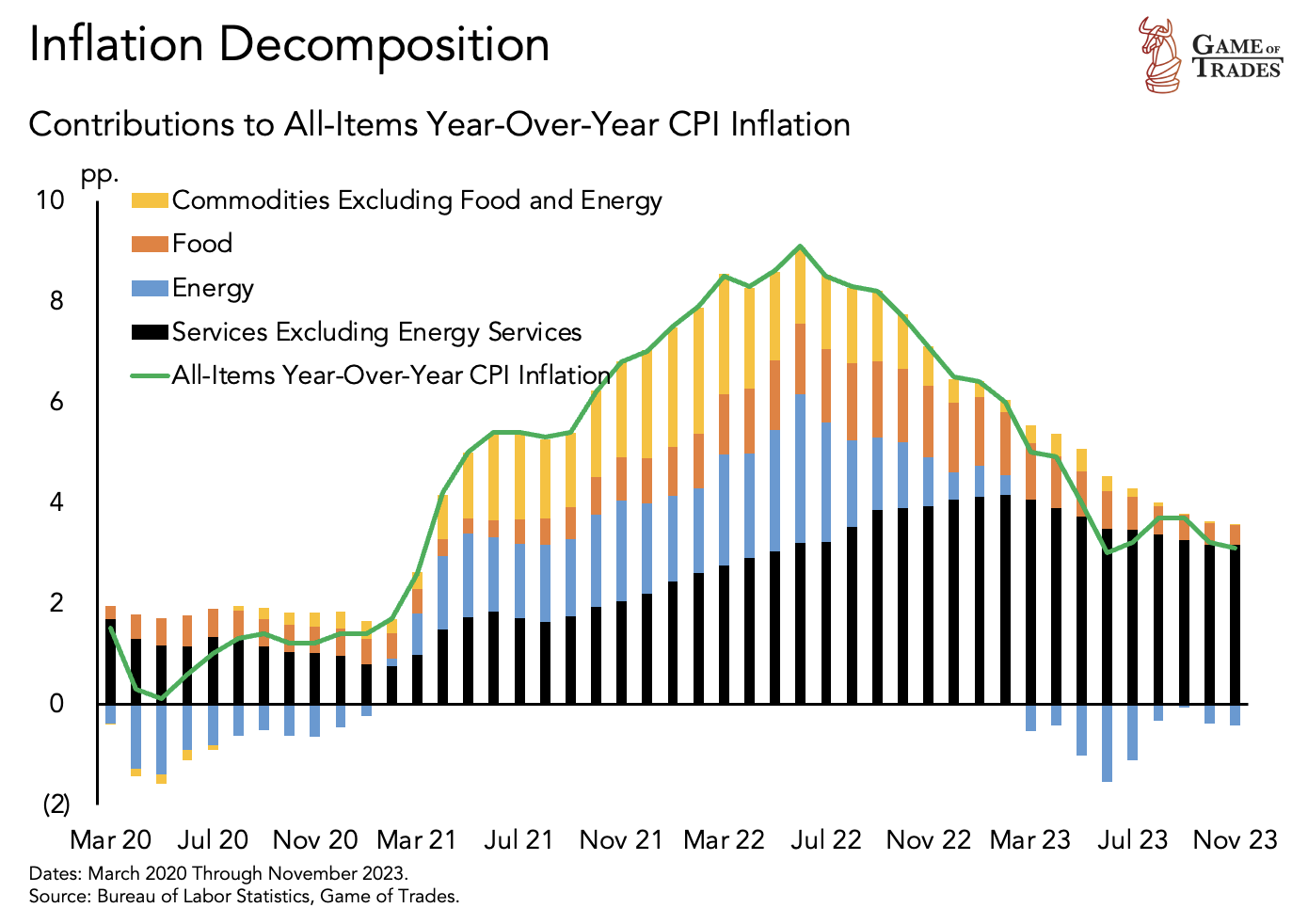
Analyzing Inflation Drivers: Services as the Persistent Component
An in-depth analysis of inflation drivers reveals a shift in dynamics. The impact of food on inflation has diminished since 2022. Today, the persistent component driving the 3% inflation rate is services, encompassing medical care, education, and transportation. Unlike the large fluctuations seen in food and gas prices, service prices undergo more gradual changes.
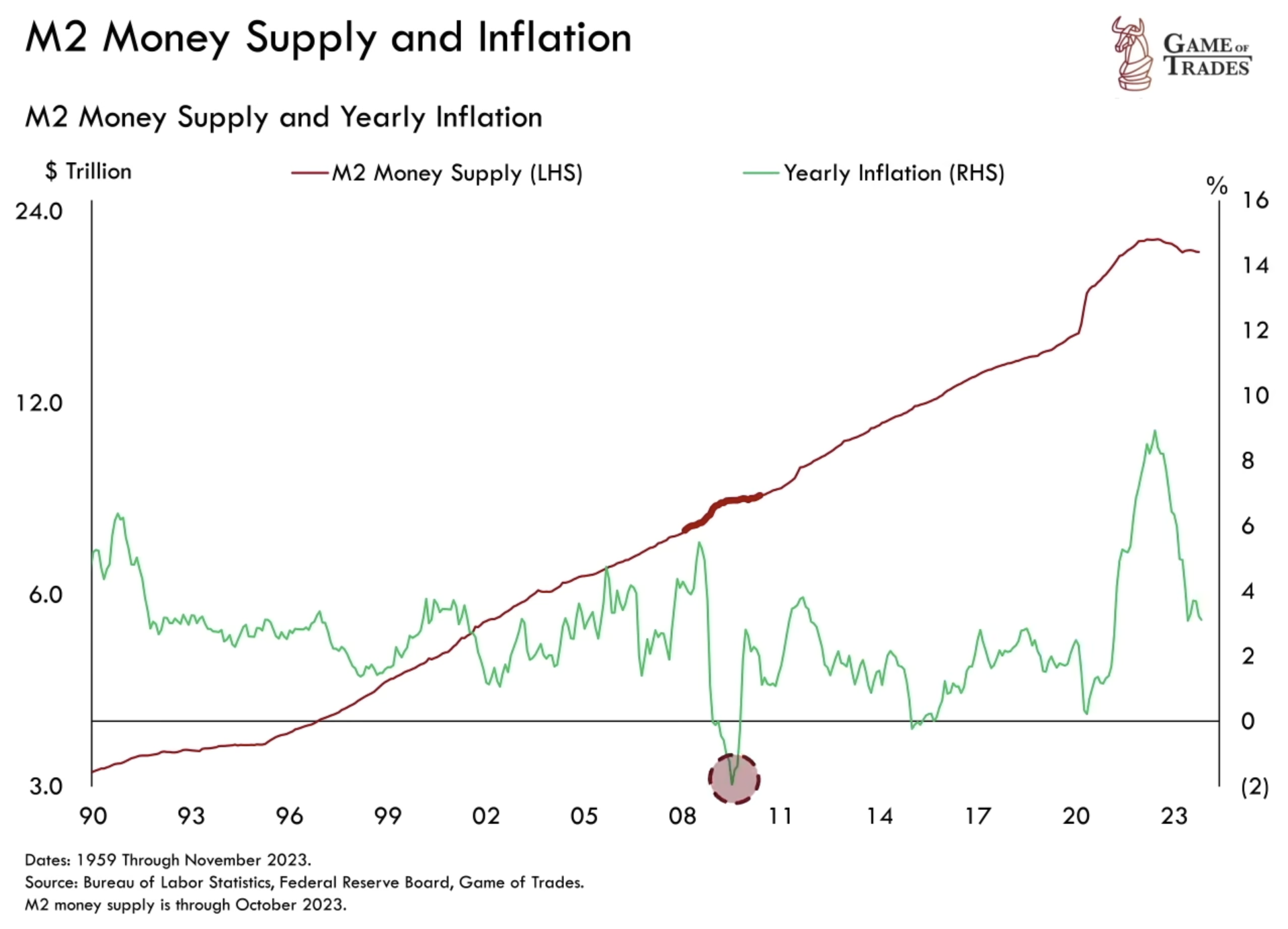
Money Supply and Its Impact
The increase in money supply during the COVID-19 pandemic significantly contributed to current inflation. The M2 spike, the most substantial in 70 years, preceded a surge in inflation to 9%. Historical patterns draw parallels to similar occurrences in the 1970s.
money
However, the money supply is now sharply contracting for the first time since the 1930s. This contraction has prompted concerns about deflation, where everyday item prices could potentially decrease. Despite a recent money supply decline, it still remains higher than pre-pandemic levels. A reversal could signal another wave of inflation. Conversely, a dip below the trend may suggest incoming deflation

However, contrary to common belief, deflation isn’t solely dependent on a contracting money supply. The financial crisis of 2009 serves as a notable example when deflation occurred despite an expanding money supply.
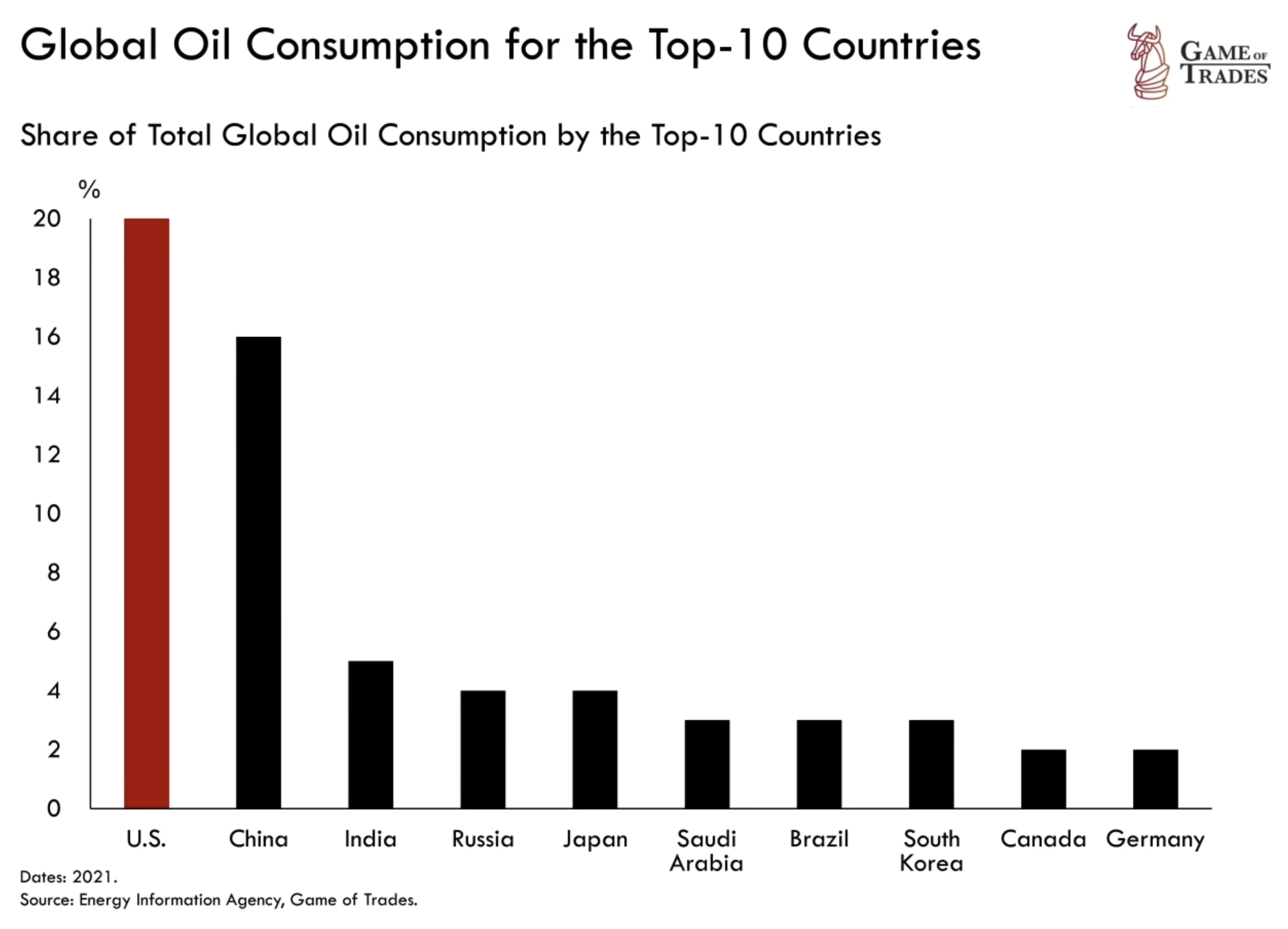
Oil Prices and the US Economy
Oil prices have plummeted by 40% since June 2022 due to dwindling demand. In 2021, booming demand drove prices higher, but today, a significant demand slowdown dominates. The United States, contributing 20% to global oil demand, emerges as the largest demand source.
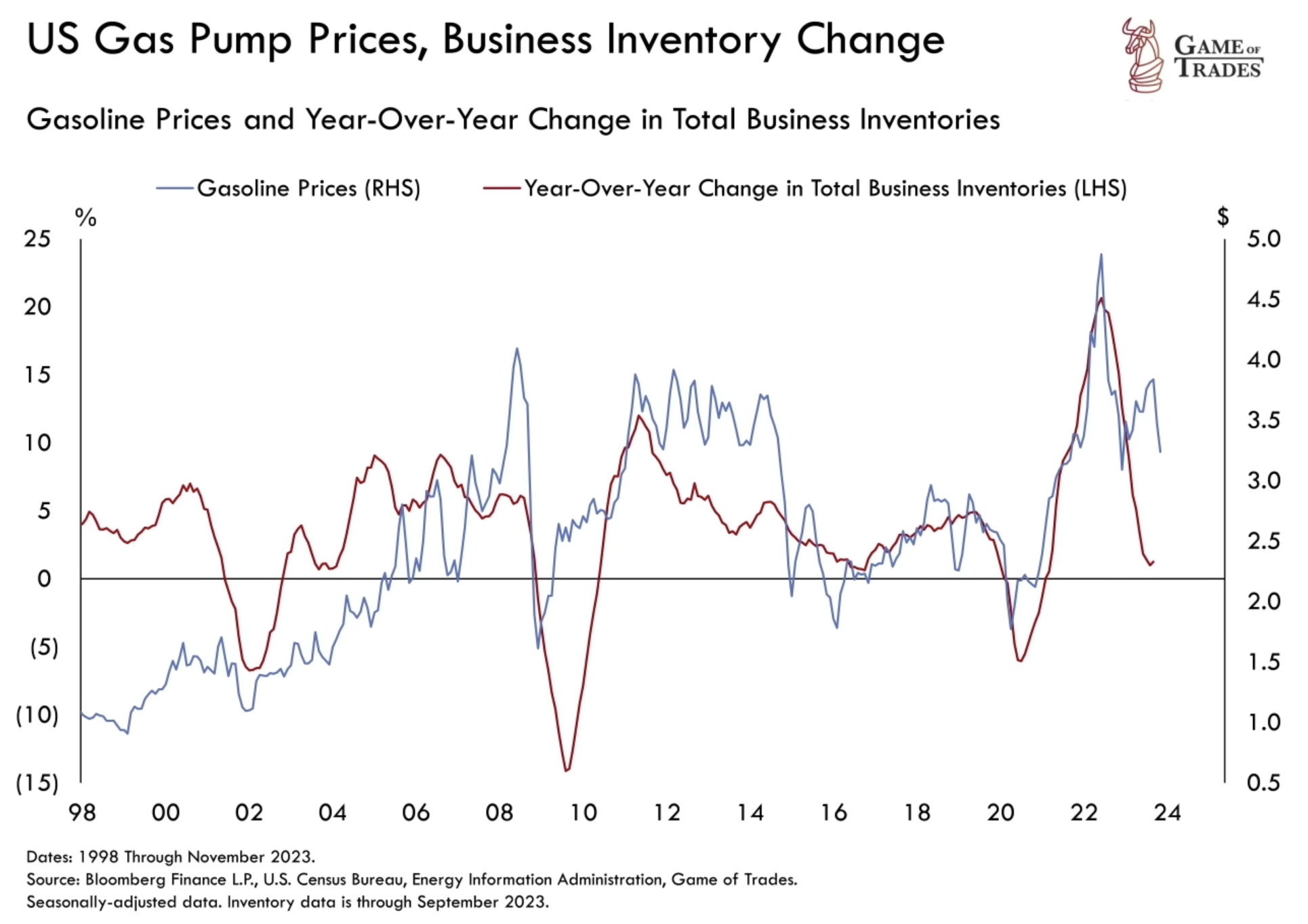
Gas prices are intricately linked to the strength of the US economy, evident when comparing them to business inventory levels. Business inventory increases drive oil prices up, while reductions lead to declines. The price of oil could rise with increased demand and inventory build-up. However, if a recession unfolds, businesses tend to reduce inventories, causing oil prices to decline. This scenario could potentially lead to deflation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding market dynamics, from asset prices to inflation and potential deflation concerns, is crucial for investors navigating the complex financial landscape. The interplay of various factors, such as agricultural prices, money supply dynamics, and oil demand, requires vigilance and adaptability. As the markets continue to evolve, staying informed about these dynamics is paramount for making well-informed investment decisions. Click here to get free trial for 7 days! Subscribe to our YouTube channel and Follow us on Twitter for more updates!
Read more: Big Rise in Interest Rates Has Massive Implications for the Economy



