The economic landscape in the United States is showing a mixed picture, with 22 states experiencing economic contractions while the overall GDP continues to grow at a healthy rate of around 3%. Despite this divergence, the stock market has been reaching new all-time highs, defying the typical relationship between economic contraction and market performance. This article aims to explore the implications of state contractions on the US economy and market, considering historical trends and key factors that may influence the current situation.
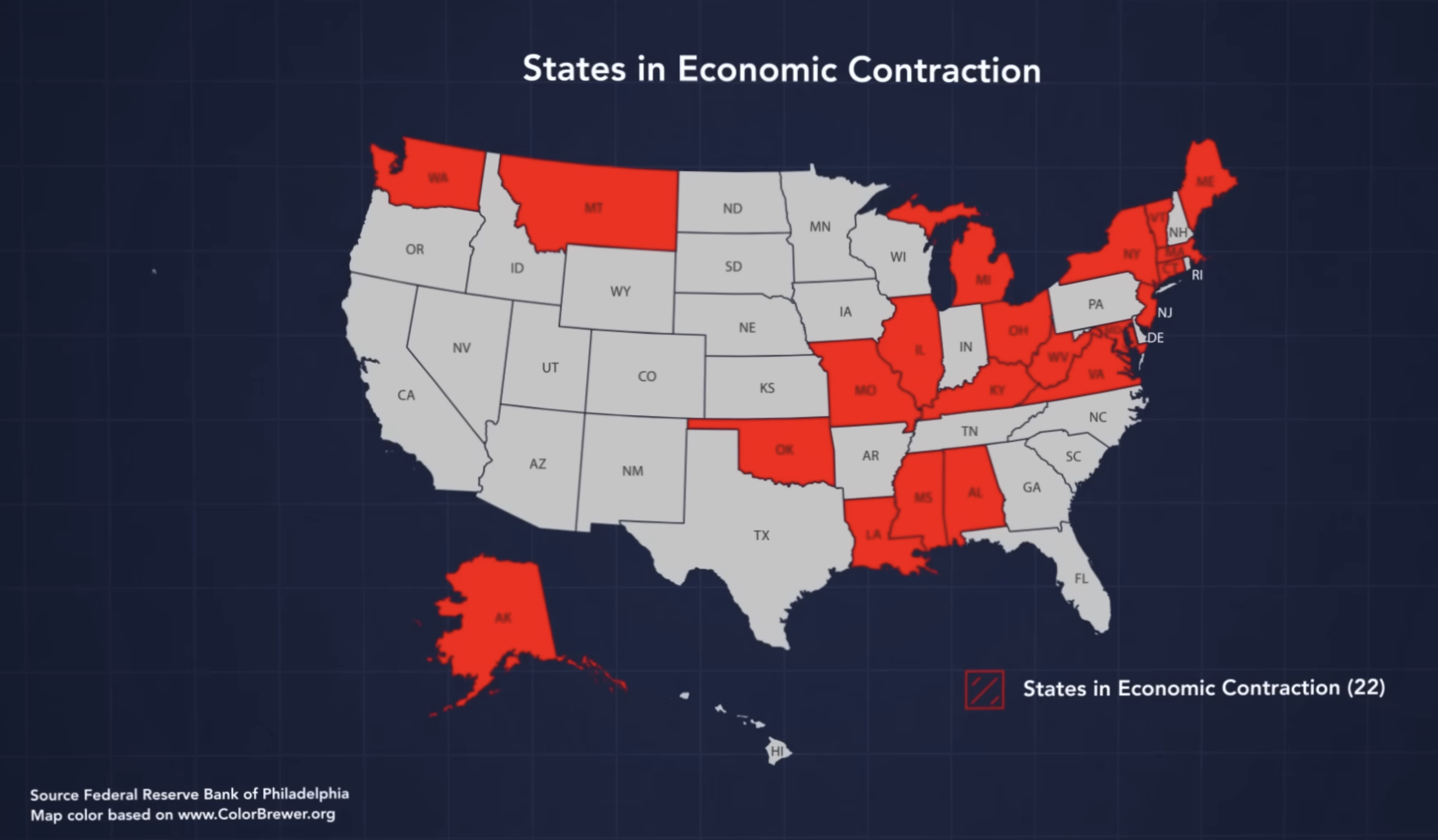
Examining State Contractions and Economic Growth
In the final quarter of 2023, nearly half of the US states, specifically 22 states, experienced economic contractions. This raises concerns about the possibility of a broader economic downturn. Traditionally, recessions occur when the majority of states enter a contraction, indicating a significant decline in overall economic activity. Currently, the US is in a precarious position, with 22 states experiencing contractions, close to the historical threshold of around 26 states that has often preceded recessions.
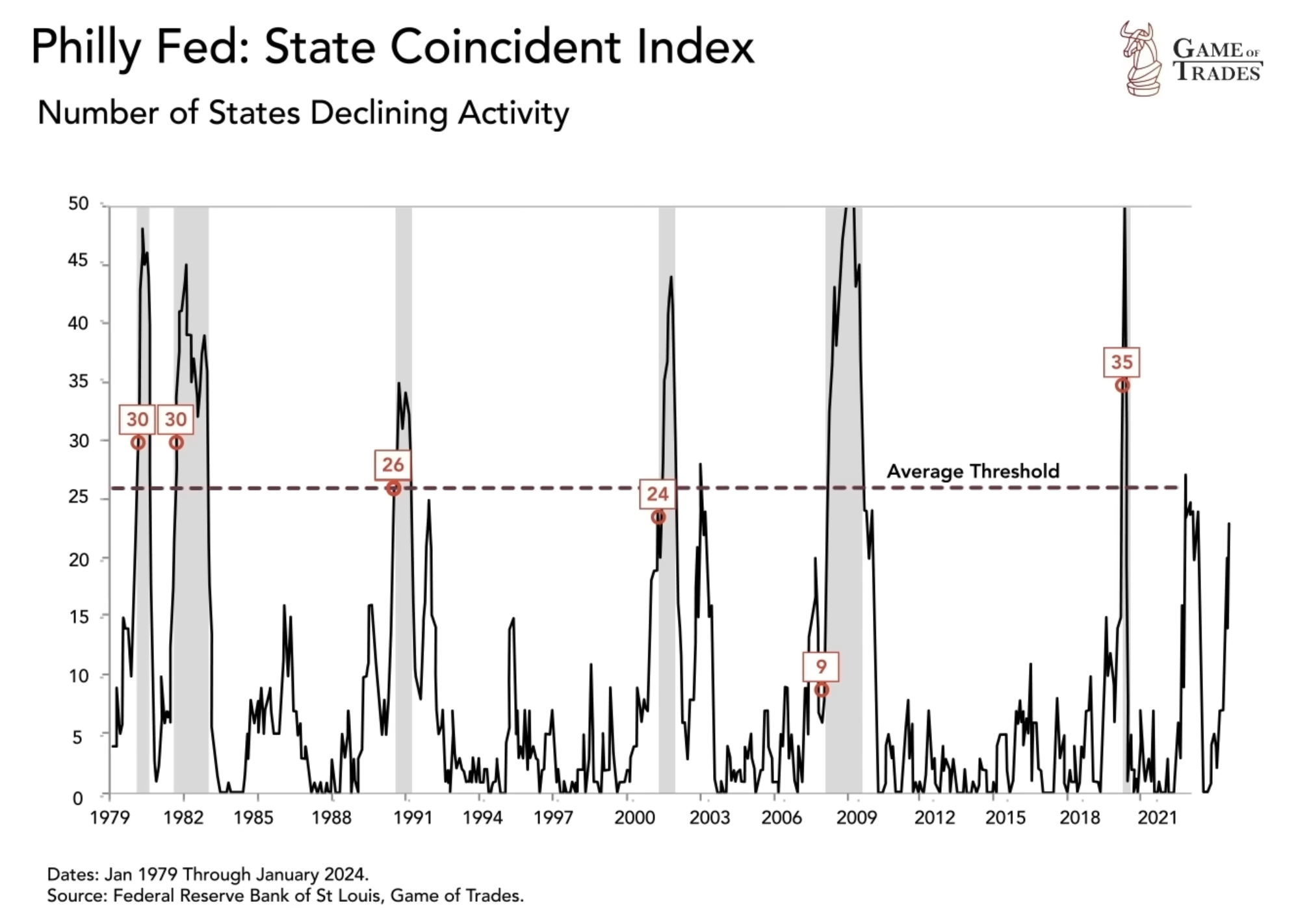
Historical Precedents and False Signals
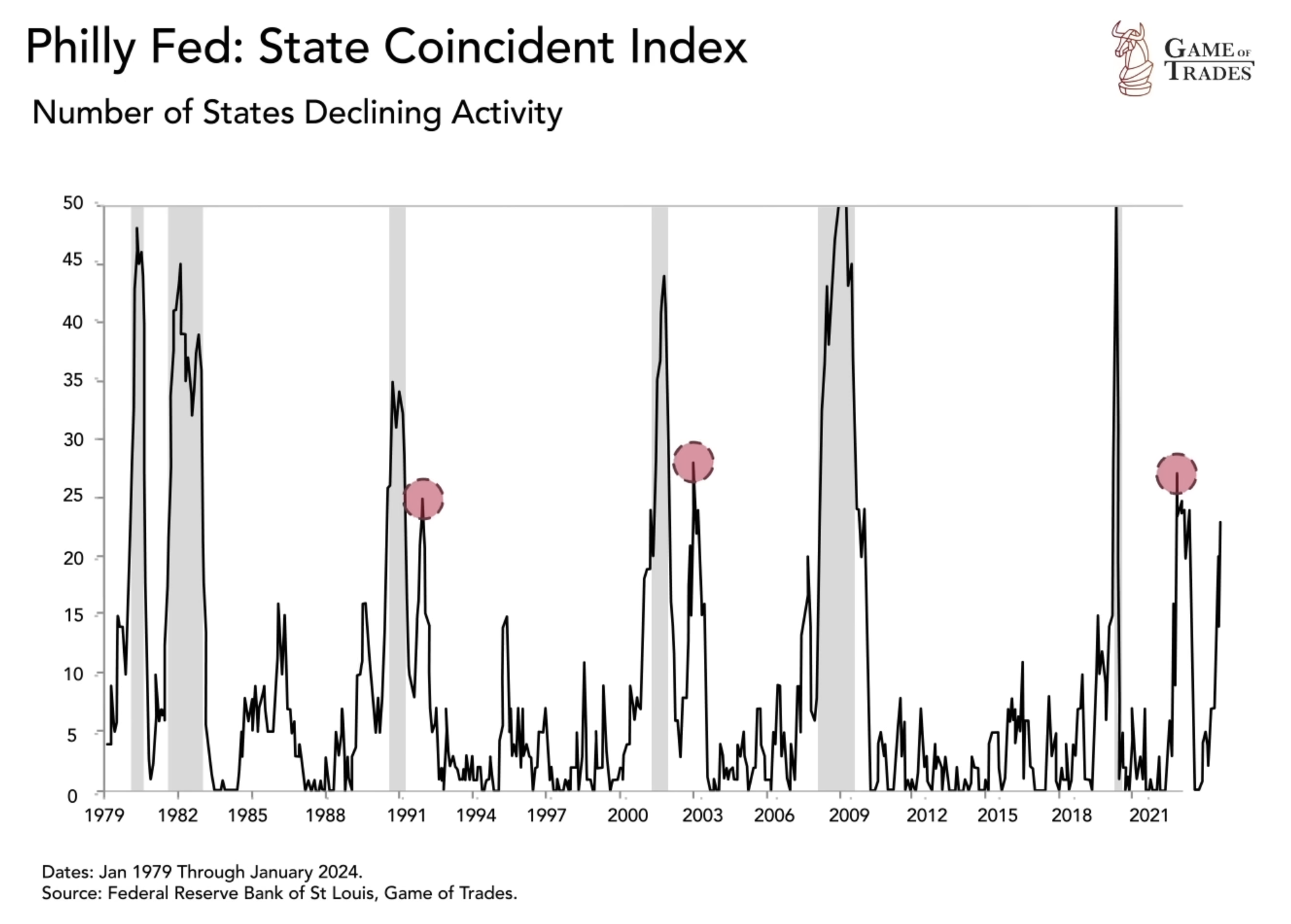
While a large number of states in economic contractions may raise alarm bells, it is essential to consider historical precedents. In 1991, 2002, and 2022, many states experienced contractions without the US entering a recession. These instances were usually a result of certain states recovering more slowly from previous recessions, rather than an indication of a broader economic downturn. However, the current situation differs significantly from those instances, making it crucial to assess the unique factors at play.
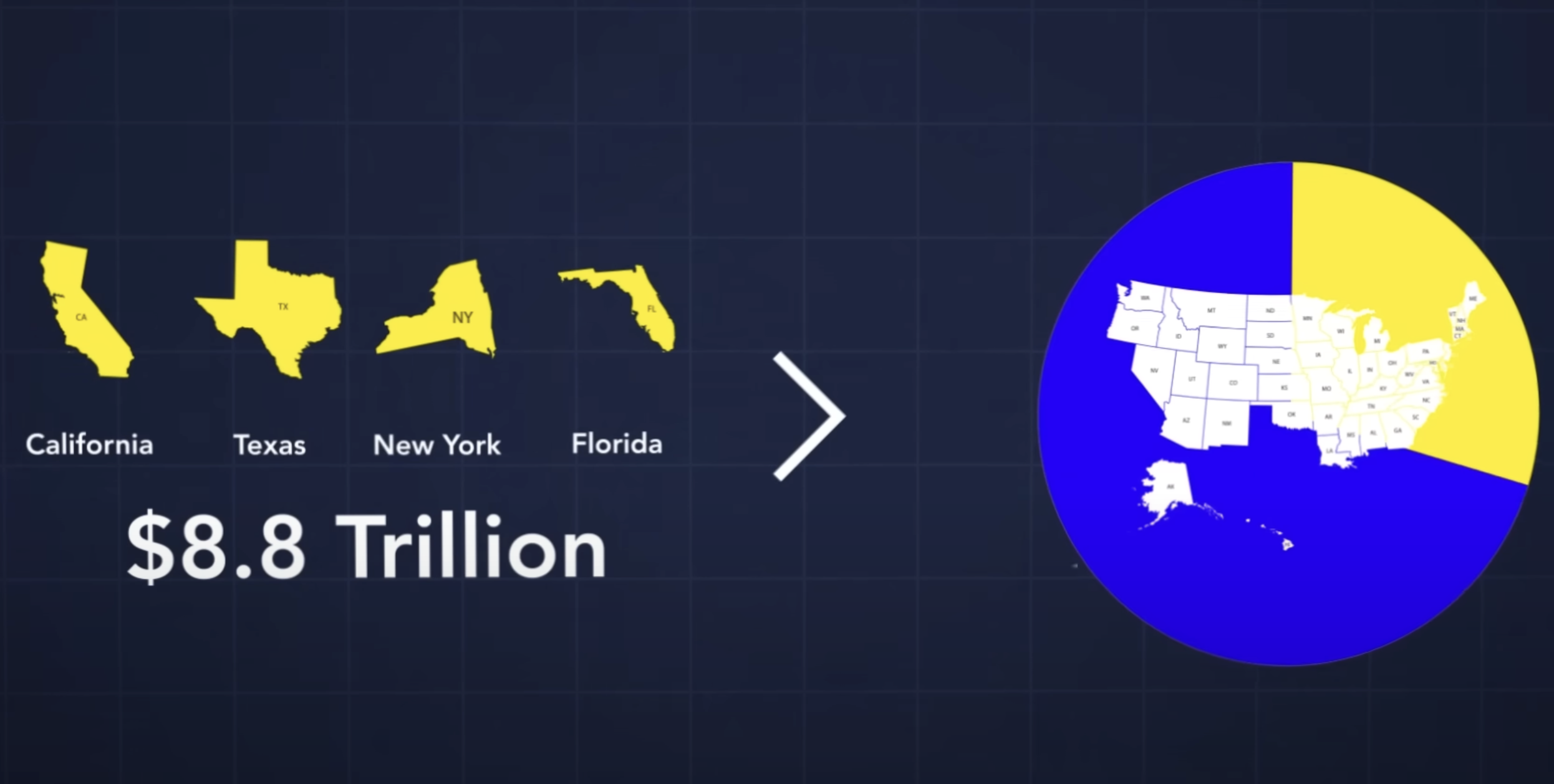
Role of Key States in Mitigating Economic Contractions
Certain states, such as California, Texas, New York, and Florida, hold substantial weight in the US economy, collectively accounting for $8.8 trillion in GDP, approximately one-third of the entire economy. While 22 states are currently in contraction, only New York is among the four largest state economies experiencing an economic downturn. California, Florida, and Texas are exhibiting steady growth, potentially offsetting the economic decline observed in other states. This suggests that the economic growth seen in the US may be driven by these states, despite the contraction in others.
Factors Affecting Economic Performance
A critical factor to consider when assessing the potential for a recession is consumer confidence. Historically, consumer sentiment tends to decline heading into recessions and recover during periods of economic expansion. In 2022, consumer confidence was extremely low, contributing to some states entering a recession. However, the situation in 2024 is different, as consumer confidence has been rising over the past couple of years. Yet, with the depletion of excess savings accumulated during the pandemic, consumer spending may be constrained, potentially hampering economic recovery.
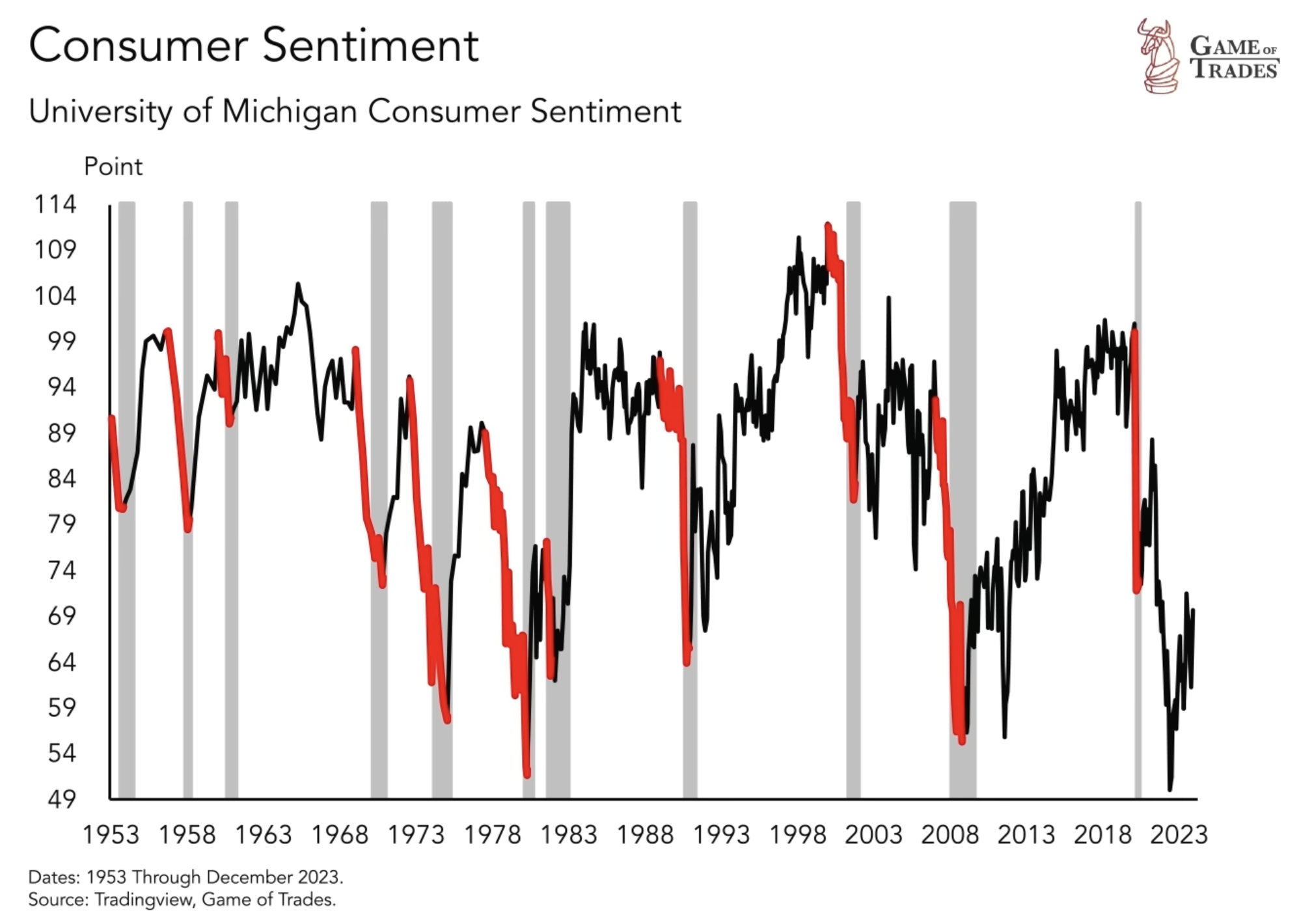
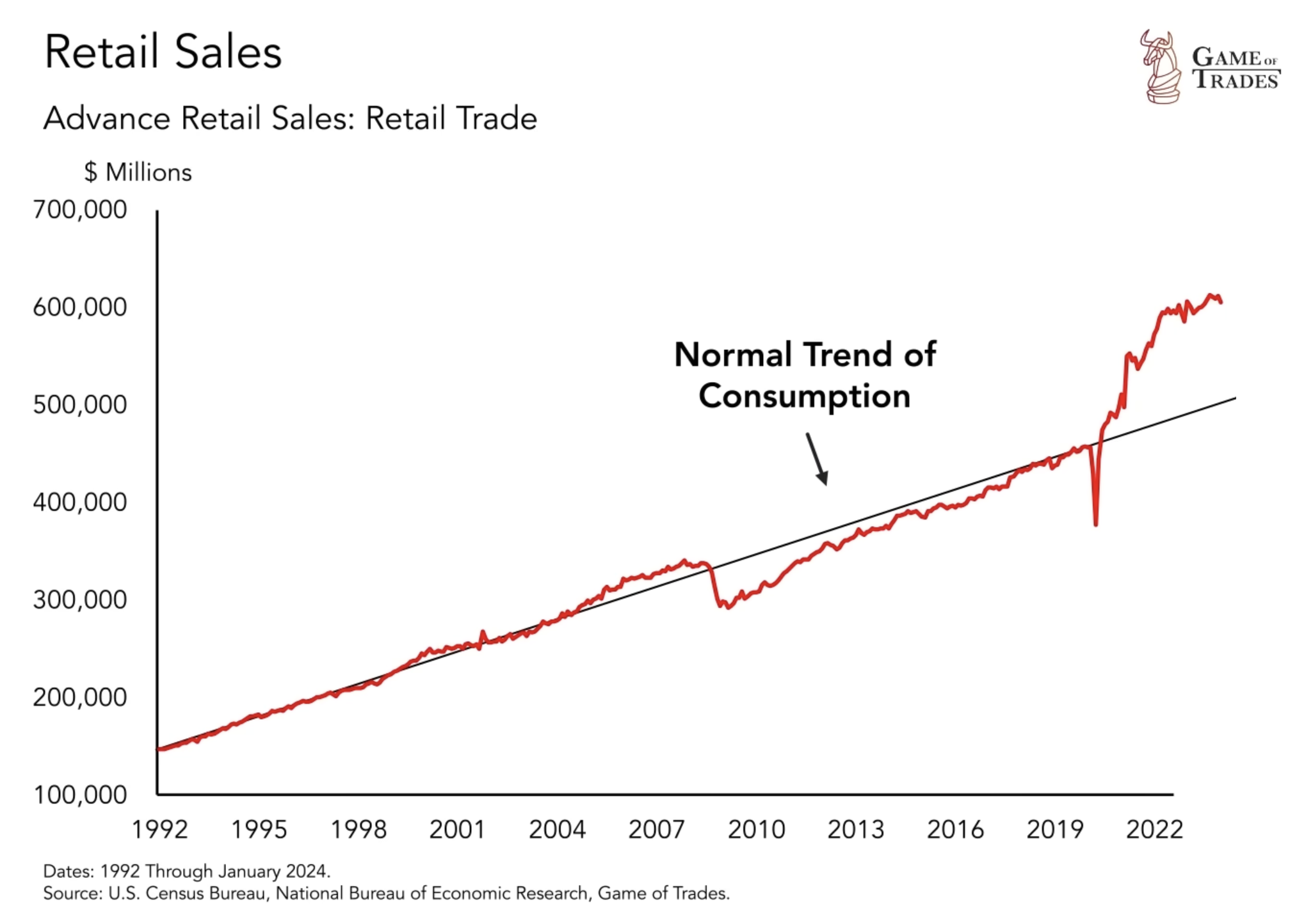
Retail Sales and the Outlook for Economic Growth
Retail sales provide valuable insights into consumer spending habits. From 2020 to 2022, retail sales surged, surpassing the long-term trend. This can be attributed to pent-up demand and catch-up spending following the economic downturn seen during the 2020 pandemic. However, in the current scenario, consumers may have already made significant purchases during the previous years, leading to a potential return to the long-term trend in retail sales. If this occurs, it could result in a prolonged period of disappointing economic growth rather than a sharp downturn like the 2008 financial crisis.
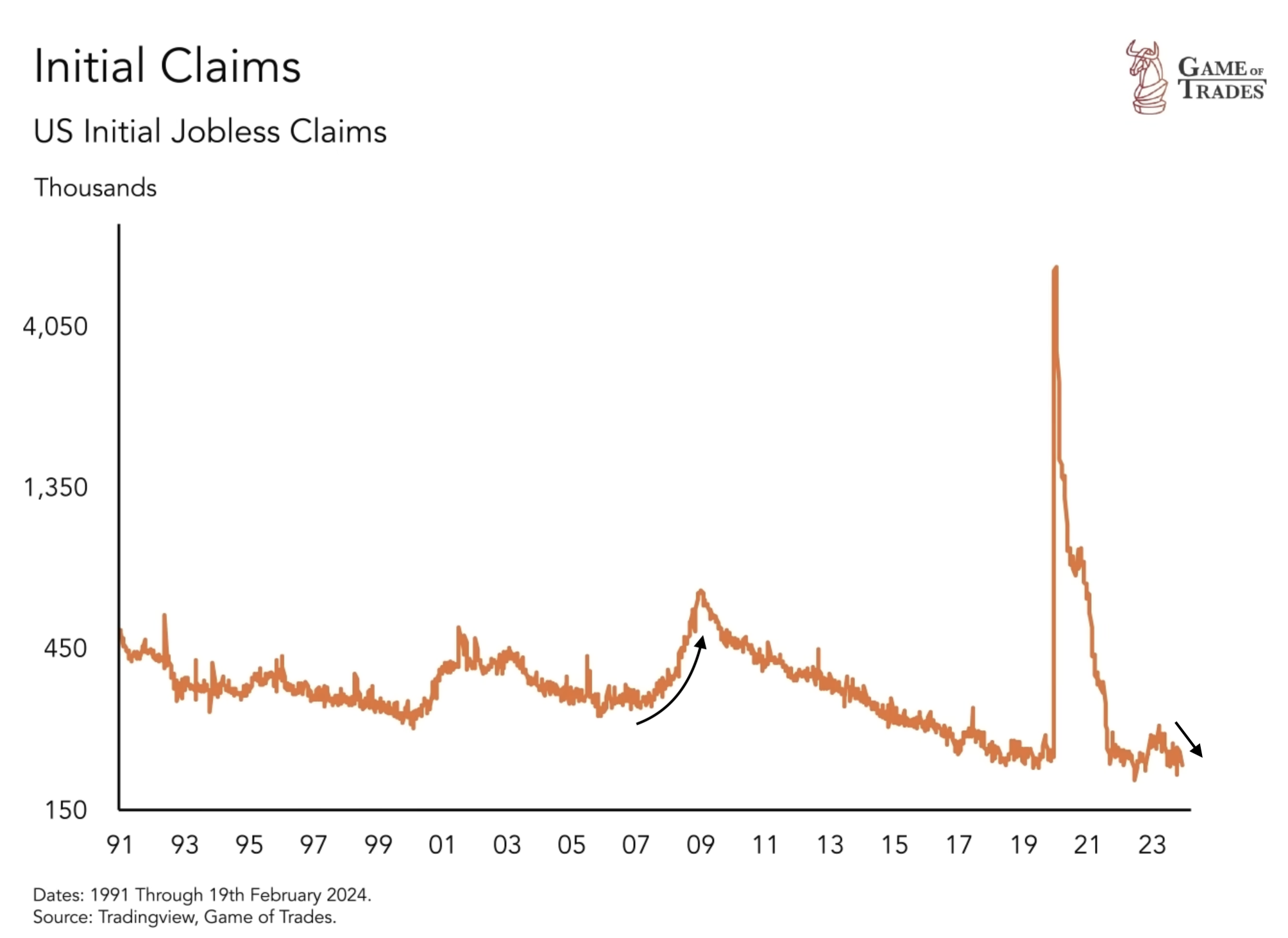
The Timing of the Recession and Labor Market Conditions
Timing a recession accurately is often challenging, given the lagging nature of different macro variables and their effects on the economy. Currently, initial claims for unemployment benefits are declining, indicating a robust labor market. This contrasts with the period preceding the 2008 recession when initial claims were rising. As long as the labor market remains strong, it is difficult to foresee a recession materializing in the United States.
Conclusion
The US economy finds itself at a critical juncture, with a significant number of states experiencing economic contractions while the overall GDP continues to grow. Although historical precedents suggest that not all state contractions lead to a recession, the current situation presents unique challenges. The contribution of key states, consumer sentiment, retail sales trends, and labor market conditions will play vital roles in shaping the economic outlook. While the timing of a recession remains uncertain, the presence of numerous states in contraction raises concerns and warrants careful monitoring of economic indicators in the coming months. Click here to get free trial for 7 days! Subscribe to our YouTube channel and Follow us on Twitter for more updates!
Read more: The Impact of Earnings on the Stock Market



